Money
Testing New Tools for Horizon Worlds Creators To Earn Money – Facebook

As part of our ongoing commitment to support creators, we’re beginning to test several new tools that will enable creators to experiment with different ways to monetize what they’re building in Horizon Worlds. While we’re launching this today as a test with a handful of creators to get their feedback, these types of tools are steps toward our long-term vision for the metaverse where creators can earn a living and people can purchase digital goods, services, and experiences.
The metaverse—by nature of its not being limited by physical space—will bring a new level of creativity and open up new opportunities for the next generation of creators and businesses to pursue their passions and create livelihoods. Creators and entrepreneurs will have more freedom to find a business model that works for them. So we’re excited to take this step today and expand further on the $10 million Horizon Creators Fund we announced last October, which we’ve been using to provide resources to Horizon Worlds creators. We’ll continue to work with our creator community and test and learn.
We’re beginning to roll out a test with a handful of creators that will let them sell virtual items and effects within their worlds. For example, someone could make and sell attachable accessories for a fashion world or offer paid access to a new part of a world.
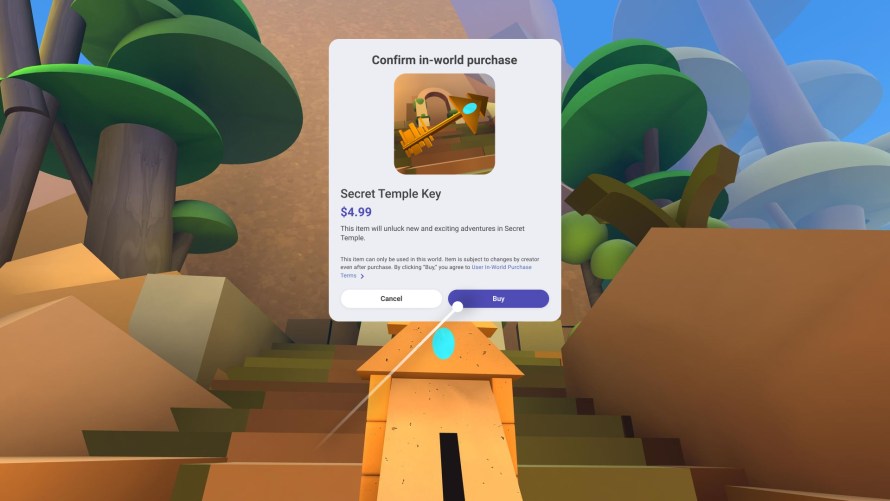
Purchasing items in Horizon Worlds is available to people 18+ in the US and Canada where Horizon Worlds is currently available. Creators selling items will see a Commerce tab and gizmo when they’re in Create mode that lets them create purchasable items.
In addition to introducing in-world purchases, we’re beginning to test a Horizon Worlds Creator Bonus program for participants in the US.
These bonuses come in the form of goal-oriented monthly programs where the creators are paid out at the end of the month for their progress toward the goal. Creator bonuses are not subject to fees and will be paid to creators in full. For now, in this limited test, creators will be rewarded for building worlds that attract the most time spent, but over time we may evolve these goals, for example, to encourage creators to adopt new tools or features we roll out.
Creators who are participating in any monetization programs, including in-world purchases and creator bonuses, are required to follow all of our policies for Horizon Worlds including the Conduct in VR Policy and Horizon Worlds Prohibited Content Policy in order to be eligible for earnings. And just as with any content in Horizon Worlds, if you see something that appears to violate our policies, you can submit a report for us to review.
While our new creator bonuses and in-world purchases tools are only testing with a handful of creators today, we’re also continuing to roll out more tools and support for all creators that make building new worlds even easier.
Money
They Call Me «Dragon» in the Crypto Community: Dragan Pajić Remarkable Journey

In the world of cryptocurrencies, Dragan Pajić, known as «Dragon,» has emerged as a prominent figure, earning him a well-deserved reputation in the Balkans and beyond. As the largest crypto influencer in the region, serial entrepreneur, and owner of the renowned 100X Club, Dragan has empowered thousands of individuals through his informative YouTube channel, demonstrating how they can multiply their investments by 100 times in the crypto market.
Through his marketing agency, DigitalPR, which has thrived for the past decade, and his rapidly-growing herbal brand called «Bonaturo,» Dragan has made a significant impact on both the digital marketing landscape and the health industry. Famous singers, actors, and public figures have not only embraced but also endorsed his brand, cementing his position as a trusted name in the market.
Dragan Pajić entrepreneurial ventures go beyond the crypto and marketing realms. He has diversified his investment portfolio, venturing into solar power plants, properties, and unicorn projects. Currently, he is an active investor and co-founder of Daopeople, the first decentralized web 3 social media platform based in Dubai.
Exciting times lie ahead for Dragan as he prepares to launch his long-awaited 100X Crypto Academy for a global audience. This groundbreaking educational platform will equip individuals with the knowledge and skills required to navigate the crypto market successfully.
Dragan Pajić achievements have not gone unnoticed. In 2018, he was recognized as one of the ten most influential young people in Bosnia.
Having accomplished his first million-dollar milestone in his twenties, he now holds the title of the Balkans’ most influential crypto influencer.
Looking toward the future, Dragan aims to empower even more young individuals, providing them with financial freedom and education in the domains of entrepreneurship, business, crypto, and investing. His ultimate goal is to become the first founder of a unicorn company (worth over $1 billion) from the Balkan region.
Connect with Dragan Pajić on his social media channels to stay updated on his latest ventures and insights
Instagram: https://instagram.com/draganpajic1?igshid=MzRlODBiNWFlZA==
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/draganpajic1?mibextid=LQQJ4d
Twitter: @Dragan_Pajic
Money
Meet the cheapest US states to buy a house

A new study analyzing Zillow data has found that the monthly median sale price of a house last year was more than $500,000 in Utah, California and Colorado — and more than a staggering $800,000 in Hawaii.
The study, conducted by Studio City realtors, found that Hawaii clocked in as the most expensive state in the U.S. for homebuyers. On the island, the average home price was $805,775 — hundreds of thousands of dollars more than the cheapest state on the list.
Studio City realtor Tony Mariotti noted that market turbulence contributed to a “significant increase” in house prices across the U.S.
Home prices went up nationwide in February after months of declines amid low inventory and a small uptick in demand — and experts have said they expect affordability will continue to be a problem for prospective homebuyers in the months ahead.
Here are the priciest and cheapest U.S. states to buy a home:
The most expensive states to buy a home
Eight states and Washington, D.C., saw a monthly median sale price of a house last year of $400,000 or higher, with Oregon sitting at that exact figure.
Washington state, Nevada, Montana and Washington, D.C., came in between $402,900 and $487,500.
California, Colorado and Hawaii were the top three most expensive, at $537,000, $537,125 and $805,775 in monthly median sale prices last year, respectively.
Costs differed in different areas within states: for example, the median monthly sale price of a house last year in California’s cheapest city of Red Bluff was $320,000 — while the ticket in its most expensive city of San Jose was $1,370,000.
Money
Don’t just hug a tree this Arbor Day — plant one, too

Nearly five years ago, Hurricane Michael became the first Category 5 storm to hit the United States in 25 years. It left a trail of destruction in its wake, and my community of Panama City — located in the Florida Panhandle — was hit especially hard. Since then, working together as neighbors and citizens, we’ve made significant progress in key recovery areas, including rebuilding key and vital infrastructure, enhancing quality of life, developing our downtown, and attracting new businesses across a mix of industries. However, one of our most important recovery efforts lies within our tree canopy restoration — an often overlooked but vital area of disaster recovery and prevention.
When Hurricane Michael uprooted nearly 80 percent of Panama City’s trees — approximately a million trees, generating 5.7 million cubic yards of debris within the city — it created serious challenges. Not only did we lose the beautiful canopy from 100-year-old oak trees, but the vital function of the trees was lost, the first of which was the absorption of groundwater. The loss of so many trees significantly increased the risk of flooding in our community,
where we now experience flooding in areas that haven’t typically flooded in the 114-year history of the city. The second function lost from the lack of trees is shade.
Trees serve to mitigate the urban heat island effect, where an entire city is warmed by concrete being heated by the sun. These increased temperatures not only result in uncomfortably hot weather but can also lead to other extreme weather events like wildfires. Since the storm, Panama City has experienced increased flooding whenever thunderstorms roll through, in addition to wildfires that consumed over 40,000 acres last year – both due in part to the damaged tree canopy and loss of trees.
-

 Leadership2 años ago
Leadership2 años agoBrain Behind Multi-Million Dollar Beauty Brands Launches Skin Care Line for Women 50+
-

 Innovation1 año ago
Innovation1 año agoMehdi Manoochehrzadeh: A Visionary Language Educator Transforming English Learning with Puzzling Method
-

 Lifestyle2 años ago
Lifestyle2 años agoDuty Free Dynamics adds yoga brand Manduka to its lifestyle portfolio
-

 Innovation2 años ago
Innovation2 años agoMelinda Herron Created a Niche for Marketing Men’s Grooming Products, Launches 103 Collection in National Retail
-

 Real Estate3 años ago
Real Estate3 años ago30 Israelis make Forbes 2022 billionaires list, led by Miriam Adelson
-

 Innovation3 años ago
Innovation3 años ago“The Millionaire Maker”
-

 Innovation2 años ago
Innovation2 años ago5 Innovative Mother’s Day Gifts for the Beauty Lover in Your Life
-

 Small Business3 años ago
Small Business3 años agoThree Questions Small Business Owners Should Ask In Creating A Workplace Culture – Forbes
